1. Add two 500g bags of whole beans to your cart
2. Add one 200g Nehi (optional roast)
3. Use the code BREWTOGETHER at checkout
The price will be automatically deducted.
The offer is valid until February 21th – or while supplies last.
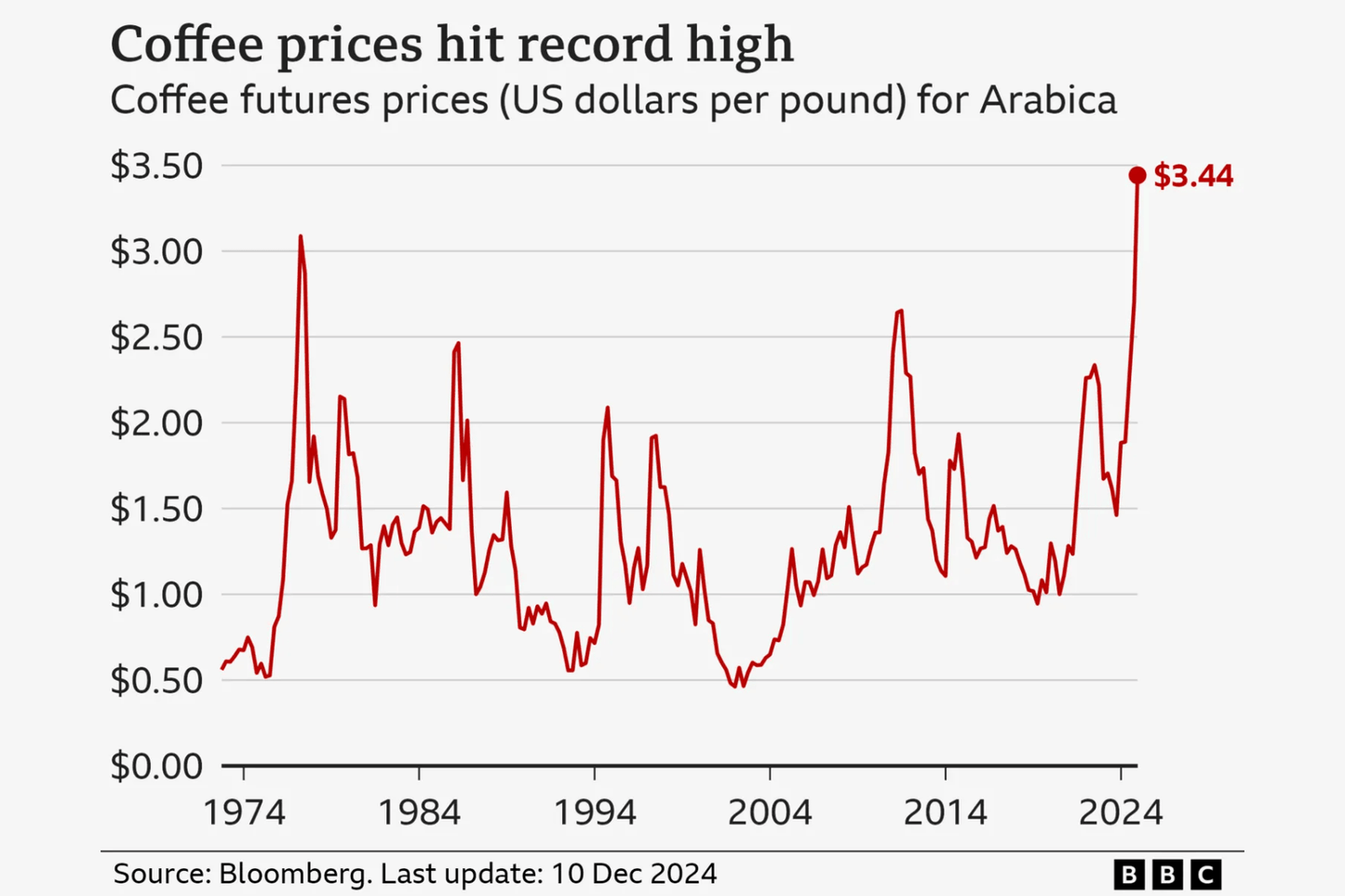
Why Ethiopian Coffee Prices Are Rising – And What It Means for You
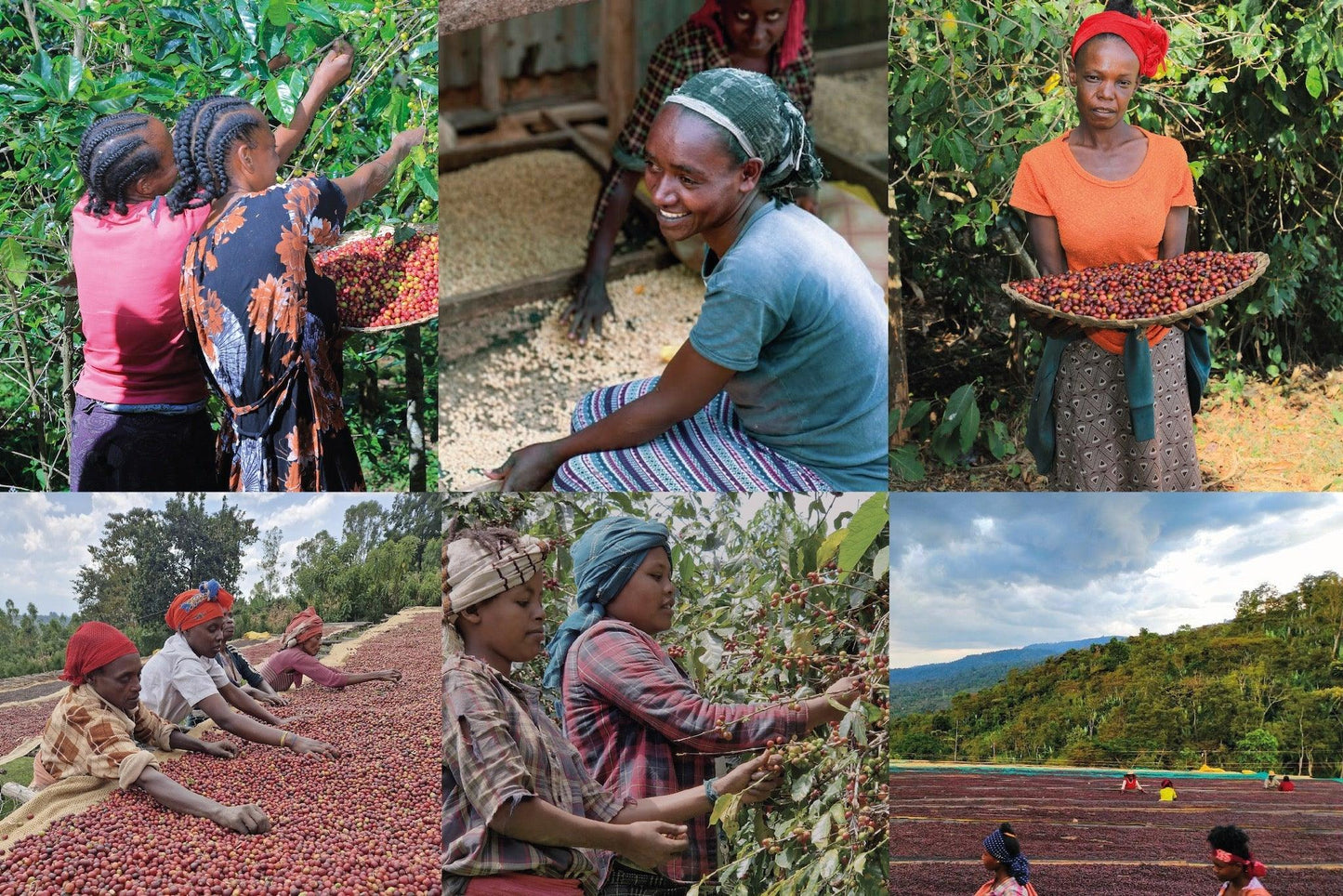
At Impact Roasters, we’ve always been committed to more than just great coffee. Our mission is to create a direct bridge between you and Ethiopian coffee farmers, ensuring fair pricing, sustainability, and exceptional quality in every cup. Today, we want to address an important shift: the rising cost of coffee worldwide and how it impacts both us and the farmers who grow your favorite brews.
Why Are Coffee Prices Increasing?
Global coffee prices have reached their highest levels since 1977, driven by multiple factors:
Climate Challenges: Extreme weather—droughts and heatwaves in Brazil and Vietnam—has reduced coffee yields. Ethiopian farmers also face erratic rainfall, rising temperatures, and shifting harvest seasons, making coffee cultivation increasingly unpredictable.
Rising Costs: Farmers are paying more for labor, fertilizers, and climate adaptation. Meanwhile, global supply chain disruptions and inflation have raised prices across the board.
Regulatory Changes: The upcoming European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) is creating uncertainty, as producers and roasters prepare for compliance, further tightening supply.
Climate Change and Its Impact on Ethiopian Coffee Farming

Ethiopia, the birthplace of coffee, has long been known for its unique, high-quality beans. However, climate change is threatening the very foundation of coffee farming in the region:
Rising Temperatures: Coffee plants thrive in specific temperature ranges. In Ethiopia, warming trends are forcing farmers to move to higher altitudes in search of cooler conditions, limiting the available land for cultivation.
Erratic Rainfall: Traditionally, Ethiopia’s coffee-growing regions have had predictable rainy seasons. Now, unpredictable rainfall patterns lead to droughts or excessive rains, both of which can harm coffee plants and reduce yields.
Increased Pests and Diseases: Warmer temperatures and shifting climates have led to a rise in coffee diseases like coffee leaf rust and pests like the coffee berry borer, which can devastate crops.
Soil Degradation: Droughts and heavy rains contribute to soil erosion, making it harder for farmers to maintain healthy coffee plants.
These environmental changes don’t just impact coffee yields—they threaten the livelihoods of smallholder farmers who rely on coffee as their primary source of income.
Why Ethiopian Coffee Is More Expensive

Ethiopian coffee, known for its unique flavors and heritage, is often pricier than coffee from other regions. Here's why:
Traditional Farming Methods: Ethiopian coffee is predominantly grown on small farms using labor-intensive, sustainable practices rather than large-scale industrial farming.
High-Quality Standards: The meticulous process of handpicking, sun-drying, and natural processing contributes to its exceptional taste but also adds to the cost.
Limited Yields: Unlike mass-producing coffee nations, Ethiopia’s production is smaller in scale, making its coffee a rare and valuable commodity.
Climate Adaptation Costs: As farmers work to combat climate change—investing in shade-grown techniques, soil conservation, and drought-resistant coffee varieties—these necessary adaptations add to the overall cost of production.
Our Commitment to Ethiopian Coffee Farmers

At Impact Roasters, we don’t just source coffee—we build lasting partnerships with Ethiopian farmers. Here’s how we continue to support them:
Impact Trade Pricing: We ensure farmers receive fair compensation, allowing them to reinvest in their land and communities.
Climate Resilience Training: We help farmers adopt sustainable farming techniques to withstand environmental changes.
Community Investments: We support initiatives in healthcare, education, and infrastructure to enhance livelihoods.
Why We’re Increasing Prices
Despite our best efforts to absorb rising costs, current market conditions require us to adjust our prices. This decision wasn’t made lightly—it’s essential to:
- Ensure fair compensation for farmers.
- Maintain quality and ethical sourcing standards.
- Invest in the long-term sustainability of Ethiopian coffee production
How You Can Support the Change
By choosing Impact Roasters, you’re doing more than enjoying great coffee—you’re investing in a sustainable future for coffee farming. Your support helps:
- Preserve Ethiopia’s rich coffee-growing traditions.
- Fund climate adaptation efforts for farmers.
- Promote transparency and fairness across the coffee supply chain.
Thank you for your continued support.
The Impact Roasters Team




